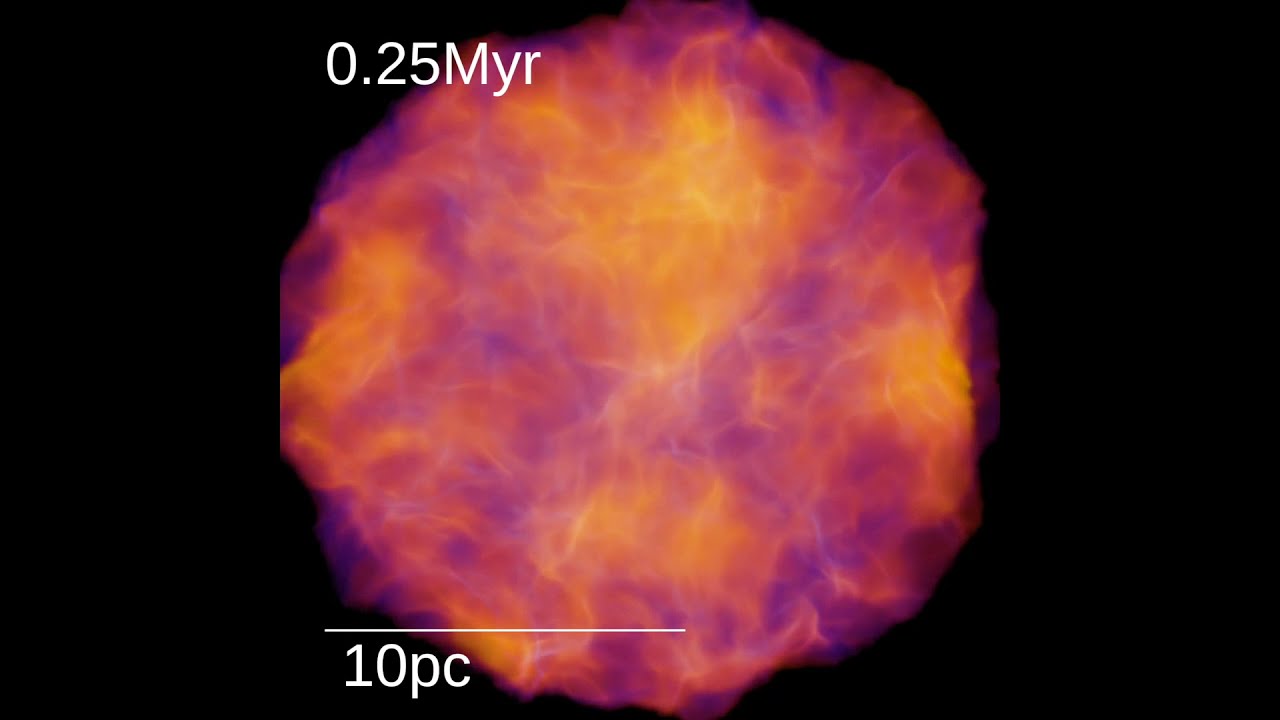
How do stars form? Most form in giant molecular clouds located in the central disk of a galaxy. The process is started, influenced, and limited by the stellar winds, jets, high energy starlight, and supernova explosions of previously existing stars. The featured video shows these complex interactions as computed by the STARFORGE simulation of a gas cloud 20,000 times the mass of our Sun. In the time-lapse visualization, lighter regions indicate denser gas, color encodes the gas speed (purple is slow, orange is fast), while dots indicate the positions of newly formed stars. As the video begins, a gas cloud spanning about 50 light years begins to condense under its own gravity. Within 2 million years, the first stars form, while newly formed massive stars are seen to expel impressive jets. The simulation is frozen after 4.3 million years, and the volume then rotated to gain a three-dimensional perspective. Much remains unknown about star formation, including the effect of the jets in limiting the masses of subsequently formed stars.
from NASA https://ift.tt/3zM1yUq
Comments
Post a Comment