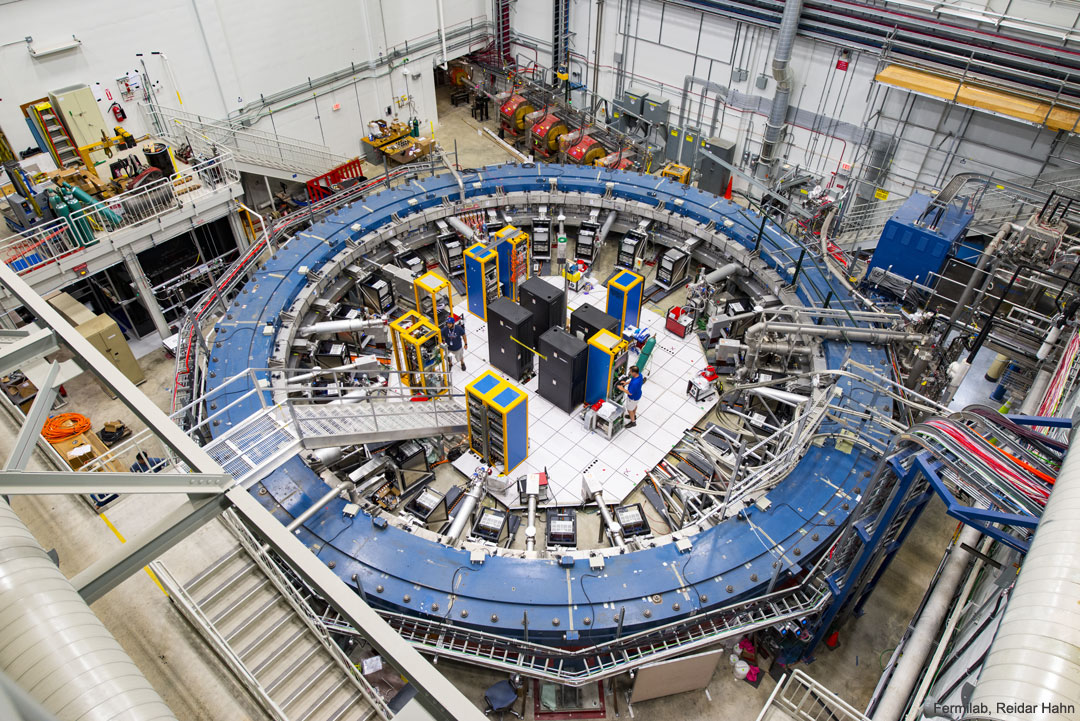
How fast do elementary particles wobble? A surprising answer to this seemingly inconsequential question came out of Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, USA in 2001, and indicated that the Standard Model of Particle Physics, adopted widely in physics, is incomplete. Specifically, the muon, a particle with similarities to a heavy electron, has had its relatively large wobble under scrutiny in a series of experiments known as g-2 (gee-minus-two). The Brookhaven result galvanized other experimental groups around the world to confirm it, and pressured theorists to better understand it. Reporting in last week, the most sensitive muon wobble experiment yet, conducted at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab) in Illinois and pictured here, agreed with the Brookhaven result. The unexpected wobble rate may indicate that an ever-present sea of virtual particles includes types not currently known. Alternatively, it may indicate that flaws exist in difficult theoretical prediction calculations. Future runs at Fermilab's g-2 experiment will further increase precision and, possibly, the statistical difference between the universe we measure and the universe we understand.
from NASA https://ift.tt/2OH3k6u
Comments
Post a Comment